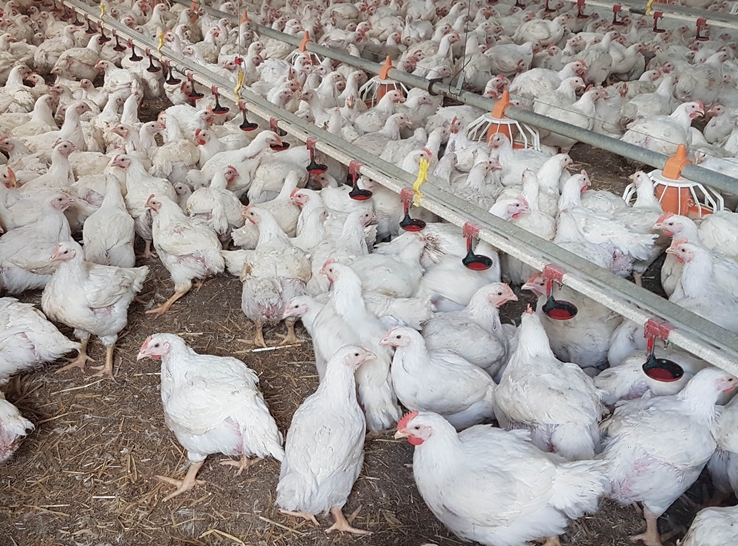
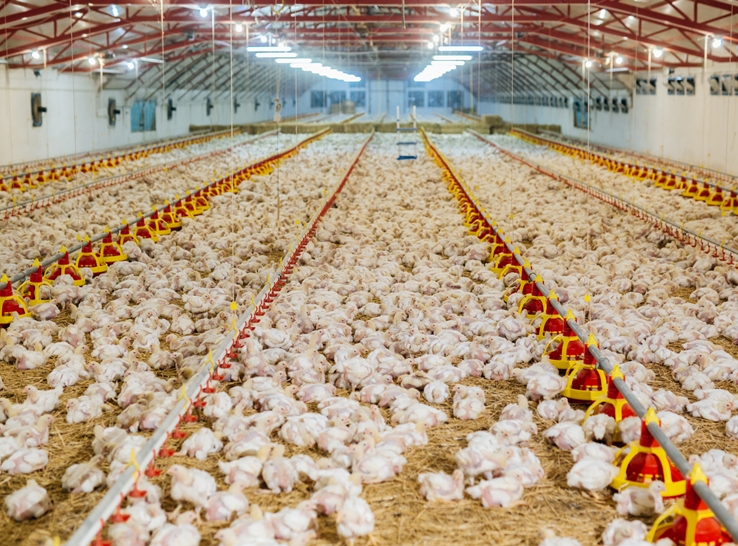
Multiple factors contribute to variable animal-welfare outcomes in outdoor-access broiler production
A “Viewpoints article”
by Allison Pullin, PhD
Prestage Department of Poultry Science
North Carolina State University
Raleigh, North Carolina, USA